- Industry
- 2 min read
Antimicrobial resistance up 40% YoY in Gujarat
An earlier report by Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) for 2021 had indicated that E Coli’s susceptibility to Imipenem (antibiotic) had dropped from 86% in 2016 to 64% in 2021. In Ahmedabad context, a study carried out at BJ Medical College from Nov 2023 to Feb 2024 had identified nine patients who were found to have Colistin-resistant bacteria.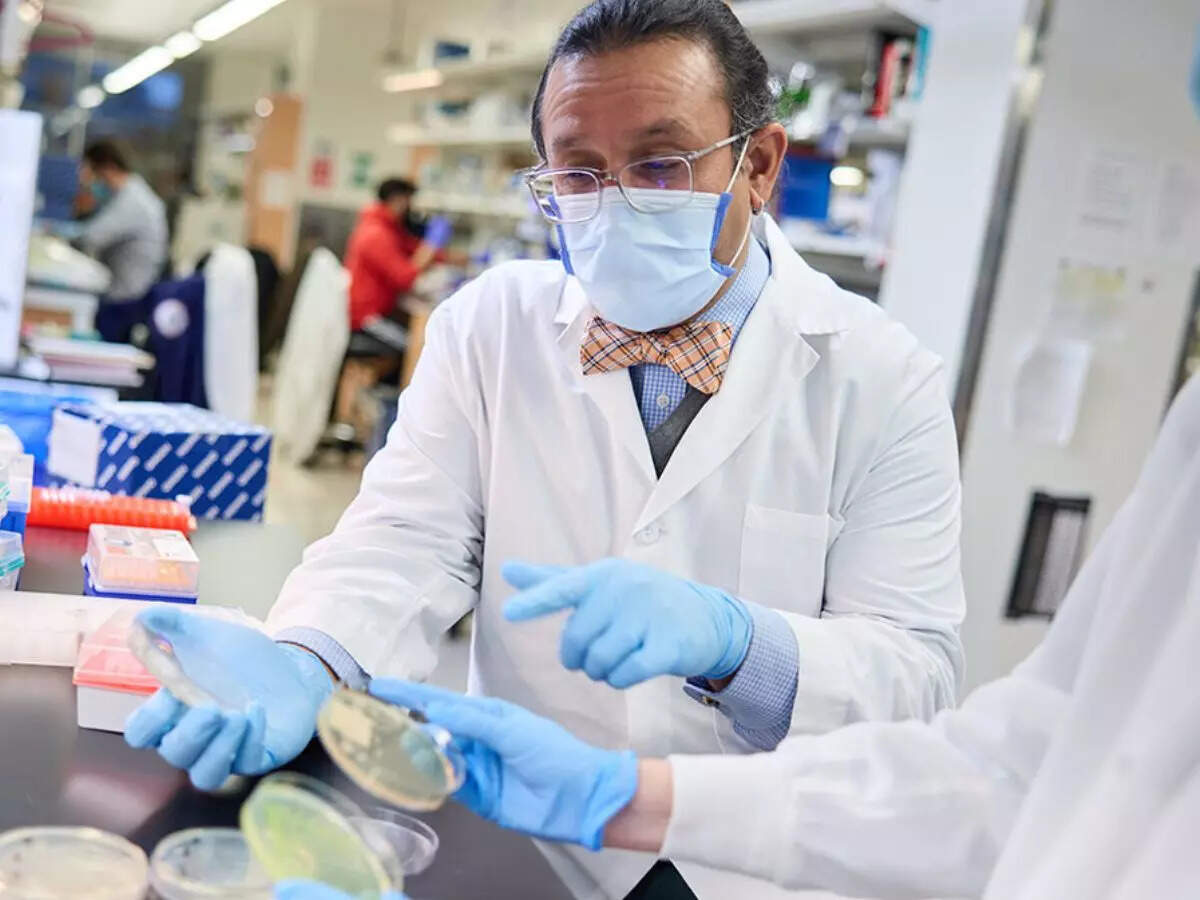
One of the reasons for the launch is year-on-year rise in AMR reporting from the state. According to the statistics of the Network Program on Antimicrobial Resistance Superbugs & One Health of the state govt, the monitoring and data collection started from April 2022. From April 2022 to March 2023, 3,643 AMR instances were reported from the state, which increased to 6,774 from April 2023 to March 2024, indicating a rise of 86 per cent . Experts, however, attribute the rise to an improved reporting from more institutions, too, along with a rise in AMR.
Dr AM Kadri, the executive director of State Health System Resource Centre (SHSRC) Gujarat, said that while the state was proactive on AMR front, the action plan implementation will ensure goals and objectives-based coordination and implementation. “One of the biggest takeaways from the action plan is coordinated efforts — so far, the stakeholders were working in their own domains. The action plan has brought them all together, be it medical, animal husbandry and the pollution control board,” he said, adding that the plan, sixth in India, follows national goals closely.
Some of the salient features of the action plan include maintaining inventory of antibiotics usage at different levels, improving awareness among doctors and other stakeholders, data-based intervention and research, and monitoring of wastewater, effluent and livestock for annual review and identification of hotspots.
Dr Urvesh Shah, professor and head of microbiology department at GCS Medical College, said that microorganisms evolve by surviving antibiotic doses and creating a resilient new generation. “Several India-based and global reports indicate a rise in AMR over years, leaving doctors with fewer options in drugs to administer. We must stop popping over-the-counter antibiotics without prescription and adopt hygiene to reduce cross-infections. We at various medical platforms have already created awareness about AMR and how to prevent it,” he said.
An earlier report by Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) for 2021 had indicated that E Coli’s susceptibility to Imipenem (antibiotic) had dropped from 86 per cent in 2016 to 64 per cent in 2021. In Ahmedabad context, a study carried out at BJ Medical College from Nov 2023 to Feb 2024 had identified nine patients who were found to have Colistin-resistant bacteria. Colistin is often considered the last resort for bacterial infections. Overall, 23 per cent were found to have multiple drug resistance (MDR).




COMMENTS
All Comments
By commenting, you agree to the Prohibited Content Policy
PostBy commenting, you agree to the Prohibited Content Policy
PostFind this Comment Offensive?
Choose your reason below and click on the submit button. This will alert our moderators to take actions